KY-004: Skillnad mellan sidversioner
| Rad 5: | Rad 5: | ||
Tactile switch är en vanlig tryckknappsmodul av samma typ som man hittar bl.a i tangentbord och möss. Den har en pulldown till jord på signalstiftet, när man trycker på knappen sluts kretsen mellan + och signalstiftet. Då strömbrytaren "studsar" bör man skriva i sk. debounce i koden. | Tactile switch är en vanlig tryckknappsmodul av samma typ som man hittar bl.a i tangentbord och möss. Den har en pulldown till jord på signalstiftet, när man trycker på knappen sluts kretsen mellan + och signalstiftet. Då strömbrytaren "studsar" bör man skriva i sk. debounce i koden. | ||
== | == Synonymer == | ||
KEYES Button Module, KY004, Momentary Button Module, 04 KEYES ARDUINO key switch module | KEYES Button Module, KY004, Momentary Button Module, 04 KEYES ARDUINO key switch module | ||
Versionen från 7 oktober 2013 kl. 15.48
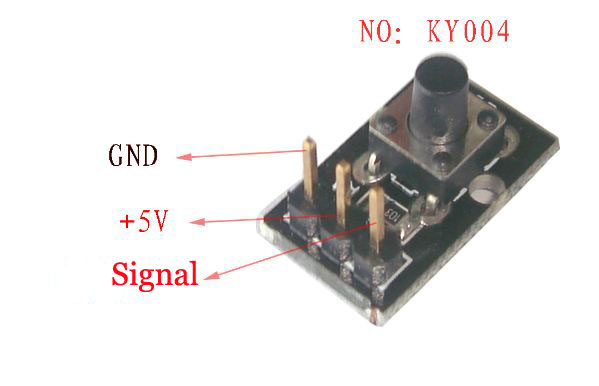
Bild
Om sensorn
Tactile switch är en vanlig tryckknappsmodul av samma typ som man hittar bl.a i tangentbord och möss. Den har en pulldown till jord på signalstiftet, när man trycker på knappen sluts kretsen mellan + och signalstiftet. Då strömbrytaren "studsar" bör man skriva i sk. debounce i koden.
Synonymer
KEYES Button Module, KY004, Momentary Button Module, 04 KEYES ARDUINO key switch module
Koppling
Arduino exempelkod
/*
Debounce
Each time the input pin goes from LOW to HIGH (e.g. because of a push-button
press), the output pin is toggled from LOW to HIGH or HIGH to LOW. There's
a minimum delay between toggles to debounce the circuit (i.e. to ignore
noise).
The circuit:
* LED attached from pin 13 to ground
* pushbutton attached from pin 2 to +5V
* 10K resistor attached from pin 2 to ground
* Note: On most Arduino boards, there is already an LED on the board
connected to pin 13, so you don't need any extra components for this example.
created 21 November 2006
by David A. Mellis
modified 30 Aug 2011
by Limor Fried
modified 28 Dec 2012
by Mike Walters
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Debounce
*/
// constants won't change. They're used here to
// set pin numbers:
const int buttonPin = 2; // the number of the pushbutton pin
const int ledPin = 13; // the number of the LED pin
// Variables will change:
int ledState = HIGH; // the current state of the output pin
int buttonState; // the current reading from the input pin
int lastButtonState = LOW; // the previous reading from the input pin
// the following variables are long's because the time, measured in miliseconds,
// will quickly become a bigger number than can be stored in an int.
long lastDebounceTime = 0; // the last time the output pin was toggled
long debounceDelay = 50; // the debounce time; increase if the output flickers
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
// set initial LED state
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
}
void loop() {
// read the state of the switch into a local variable:
int reading = digitalRead(buttonPin);
// check to see if you just pressed the button
// (i.e. the input went from LOW to HIGH), and you've waited
// long enough since the last press to ignore any noise:
// If the switch changed, due to noise or pressing:
if (reading != lastButtonState) {
// reset the debouncing timer
lastDebounceTime = millis();
}
if ((millis() - lastDebounceTime) > debounceDelay) {
// whatever the reading is at, it's been there for longer
// than the debounce delay, so take it as the actual current state:
// if the button state has changed:
if (reading != buttonState) {
buttonState = reading;
// only toggle the LED if the new button state is HIGH
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
ledState = !ledState;
}
}
}
// set the LED:
digitalWrite(ledPin, ledState);
// save the reading. Next time through the loop,
// it'll be the lastButtonState:
lastButtonState = reading;
}